The allure of the Arabic language, characterized by its elegant script and profound historical roots, enchants a vast global audience. Yet, for individuals eager to engage in Arabic typing, a realm brimming with new possibilities unfolds. This piece delves deep into the intriguing domain of the Arabic keyboard layout, shedding light on its distinctive architecture and operational capabilities. We will uncover how this keyboard facilitates self-expression in the exquisite Arabic tongue, facilitates seamless navigation through the digital sphere, and fosters connections with Arabic-speaking communities worldwide. Whether you’re a proficient Arabic communicator or embarking on your linguistic journey, brace yourself to unravel the mysteries concealed within the Arabic keyboard!
Discover the Unique Features of the Arabic Keyboard Layout
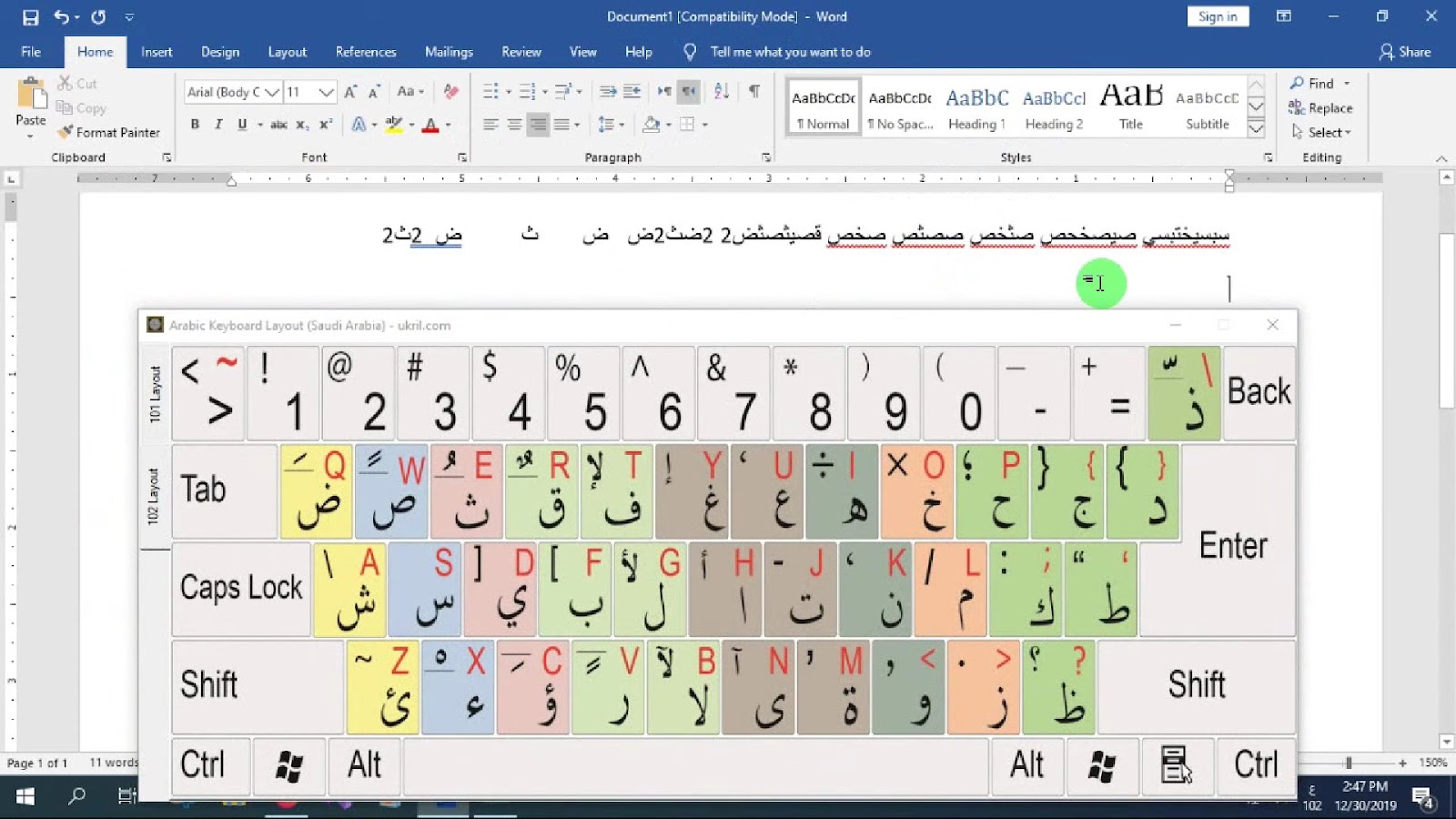
The Arabic keyboard layout seamlessly facilitates the nuanced writing system of the Arabic language, which is inherently written from right to left. This layout, while different from the familiar QWERTY setup used in English and numerous other languages, adheres to an arrangement of letters and symbols that is intuitive to Arabic script.
Navigating the Right-to-Left Orientation
An immediately apparent difference in the Arabic keyboard layout is its right-to-left orientation, mirroring the natural flow of Arabic script. This unique orientation is an inherent requirement of the Arabic language but could seem unusual to those accustomed to left-right scripts.
Comprehending Additional Letters
The Arabic language consists of several alphabet characters distinct from English, such as ة (ta marbuta), ذ (dhal), ص (sad), and ض (dad). To ensure typing in Arabic is as streamlined as possible, these unique letters are incorporated into the Arabic keyboard layout for convenient access.
Grasping Special Characters
The Arabic keyboard layout goes beyond mere letters, integrating special characters and diacritics crucial to Arabic script, such as ـَ (fatha), ـُ (damma), and ـِ (kasra). These elements are important for indicating vowel sounds within words, enhancing the distinctive structure and sound of the Arabic language.
Utilizing Dual-Function Keys
Interestingly, certain keys within the Arabic keyboard layout feature dual functionality. This feature allows users to impart both letters and symbols on screen by hitting the Shift key or executing combination shortcuts. This clever design aspect helps save time and increase productivity, especially during extensive typing sessions.
By understanding these key features of the Arabic keyboard layout, users can quickly master Arabic typing, skillfully navigating between letters, symbols, and diacritical marks.
Decoding the Arab Keyboard Layout: A Comprehensive Guide
The Arabic keyboard layout is meticulously curated to cater to the unique characteristics of the Arabic script. Unlike the English-oriented QWERTY layout or those designed for other left-to-right scripts, this layout incorporates the distinct arrangement of Arabic letters and symbols, following a right-to-left narrative.
Exclusive Features of the Arabic Keyboard Layout
- Embracing the Right-to-Left Script: Arabic is one of the few languages written from right to left, and the Arabic keyboard naturally mirrors this unique characteristic. This contrast is instantly discernible to individuals experienced with left-to-right scripts, and mastering this reversal is the first step towards fluency in Arabic typing;
- Accommodating Unique Arabic Letters: The Arabic language is enriched with letter forms absent in the English language alphabet, such as ة (ta marbuta), ذ (dhal), ص (sad), and ض (dad). The Arabic keyboard layout prominently features these unique forms, ensuring that users can access these vital letters without a hitch;
- Incorporating Essential Special Characters: Beyond the standard letters, the Arabic keyboard layout assimilates crucial special characters and diacritical marks used in the Arabic script. Key examples include ـَ (fatha), ـُ (damma), and ـِ (kasra) – representing vowel sounds and adding depth to the language’s phonetics;
- Unveiling Dual-Function Keys: The Arabic keyboard layout showcases ingenious dual-function keys, permitting users to yield both letters and symbols using the same keys. Engaging the Shift key or appropriate keyboard shortcuts unlocks these secondary functions, a potent tool for enhancing typing efficiency and speed.
Practical Advice for Navigating the Arabic Keyboard Layout
Acclimating to a New Keyboard Terrain
One of the first steps to proficiency in Arabic typing involves understanding the unique layout of the Arabic keyboard. Practising basic words and gradually progressing to complex sentences effectively enhances typing speed and improves accuracy.
Understanding the Role of Diacritics
The use of diacritical marks, or harakat, in Arabic text adds essential details to pronunciation and grammatical contexts. Therefore, being able to access and use these marks aptly during typing can significantly enhance the conveyance of meaning.
Harnessing the Power of Shift Functions
The Arabic keyboard layout houses multiple functions within single keys, accessible via the Shift key. Mastery over this functionality reveals capital letters, punctuation marks, and special symbols vital to Arabic text composition.
Optimizing Keyboard Settings for Personal Comfort
The Arabic keyboard layout can be modified to suit an individual’s typing habits or comfort. The adjustment of settings such as key repeat rate or keyboard layout variations can enhance typing proficiency and provide a tailored typing experience. Data input language switching can also assist in seamlessly transitioning between language inputs.
Conclusion
The Arabic keyboard layout is specifically crafted to support a distinct writing style that flows from right to left, integrating diacritics seamlessly. This layout not only facilitates typing in Arabic but also allows for the inclusion of Latin characters, making it a versatile option. Whether you choose the standard Arabic (101) or Arabic (102) layout or decide to explore the phonetic alternative, you’ll find a solution that suits your requirements. With some dedicated practice, you’ll soon master typing Arabic effortlessly.